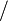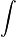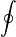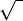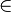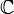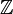Suggestion of Mid-Term Examination for 15th Batch
|
Chapter
|
example
|
Exercise
|
|
3
|
8,7,10
|
3(1)(2),
5(i)(iv), 7(i)(ii), 11(v), 16(i)(ii)
|
|
4
|
6,10,11,15
|
1(iv)(vii),
4(i)(iii), 7(i)(iii), 10(i)(ii), 12(i)(ii)
|
|
5
|
4,5,7,13
|
2(i),
3(i), 4(i)(iv), 5(i)(iii), 7(i), 8(i), 9(iii), 15
|
|
8
|
1,5,11
|
10,11,13,24,25
|
|
9
|
6,10,11
|
9(viii)(xiii),
2(i), 3(i)(iii), 6(i)(vii), 9(i)(ix)(xii)
|
|
11
|
7(ii)(v),
8(ii)(iii)
|
2(i)(iv),
4(i)(iv), 7(i), 9(i), 12(i), 14(i)
|
|
12
|
3,5,6,8
12,17,18,20
|
13,15,20,21,26-30
|

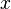
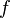




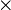 or
or 
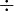 or
or